Digitization is being driven by future technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, Big Data, or Blockchain technology. While software robots and intelligent, self-learning systems are gaining increasing interest and are known to many users, blockchain technology is often a synonym for cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are only a marginal phenomenon and the technology has the potential to revolutionize entire branches of industry.
What does blockchain mean?
The blockchain is a comparatively new technology that, at first glance, represents a kind of digital register that is highly secure and works without a central instance. This digital register fulfills the same functions as a database and stores individual transactions. Digital database systems already existed before online banking was introduced, so blockchain technology is not very revolutionary in the first step.
This impression is not correct, however, because the blockchain enables the storage, processing, management, and sharing of data in a public and accessible database. All transactions occurring in a network are stored in transaction blocks and encrypted using a hash function. After encryption, this block is saved and attached to the previous one. Figuratively speaking, the stored blocks are lined up in a chain.
What is blockchain technology?
The basic idea of the blockchain can be traced back to the bitcoin whitepaper. This was published by an unknown IT expert under the pseudonym “Satoshi Nakamoto” and describes a decentralized system. Above all, the problems with dealing with monetary values - also known as fiat money – were the reason to develop a system for the decentralization of payment transactions. Banks in particular use the money paid in by customers to issue new loans. This principle increases the amount of money in the market, resulting in an overvaluation of individual assets. The global economic crisis of 2008 made it clear what consequences an overvaluation of real estate and the granting of insecure loans have.
The digital register presented by Nakamoto relates to the transfer process of information and values. A decentralized approach is to take control of this information from individual institutions and pass it on to a community or network of like-minded stakeholders. In a blockchain, all information is publicly visible and the transactions are traceable.
How to prevent access to the data of another user?
In order to prevent access to the data of another user, all accounts of a blockchain are anonymized. Only the alphanumeric address enables an account to be identified. In order to do justice to the approach of decentralization, the stored data is not stored centrally on a single server. Instead, the blockchain acts as a decentralized register and is stored on numerous computers around the world. These are connected via the Internet and each has a complete account book.
This approach results in one of the greatest advantages of the technology, as manipulation of data, becomes comparatively unlikely. If a user changes the stored information, all other users can recognize the fraud. By comparing the different blockchain versions, fraudsters can be identified and banned from the network within a very short time. The Bitcoin whitepaper sees this approach as a way of preventing the unauthorized use of the capital made available. This offers the user a very high level of security. Overall, blockchain technology focuses on security, transparency, anonymity, and decentralization.
How does blockchain work?
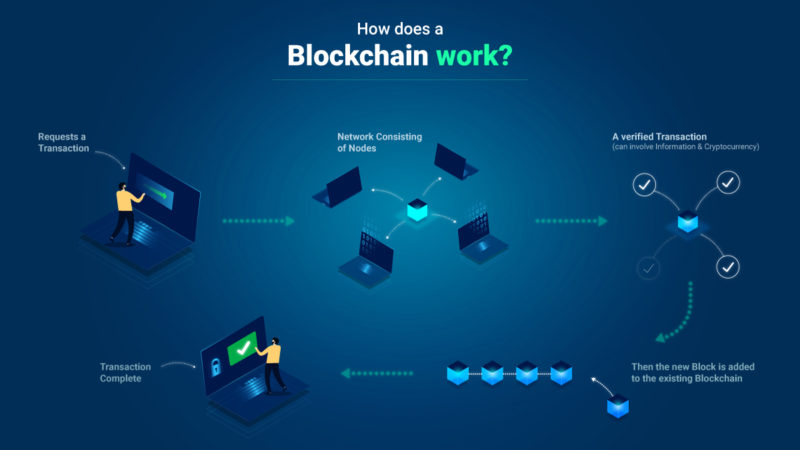
Probably the best-known blockchain is the Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, i.e. a digital means of payment. All transactions on the network are stored in blocks using a proof-of-work algorithm. This takes on a fundamental role within the blockchain because in addition to storing the blocks, all transactions are verified and new bitcoins are created.
The corresponding algorithm is located in software that can be used by computers in the Bitcoin network. With the help of the algorithm, individual transactions in the network are encrypted and stored in a block. This process is also known as mining.
A lot of computing power is required for mining, which the miners provide in return for a reward. However, since not an infinite number of transactions take place at the same time, the miners are in competition with one another. For this reason, the computing power and the corresponding power requirements play a particularly important role in a blockchain with a proof-of-work algorithm. After the block has been completed, it is stored in the blockchain and distributed to the other participants in the network.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of blockchain technology?
Now that the principle of the blockchain has been clarified, we can now take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of this technology:
Benefits
- In principle, the stored data is anonymized and encrypted, which makes the use of blockchain in many areas, such as B. makes supply chains, financial transactions, or Industry 4.0 applications attractive.
- The stored data can only be accessed if the correct key is used.
- If a blockchain is used in the company, large amounts of data can also be collected and then analyzed.
- By involving different users, the collected data can be verified particularly quickly and reliably.
- Since all transactions of a process are stored in a blockchain, they can also be traced afterward. This procedure allows a particularly high degree of transparency, for example in the context of error analysis.
- If the blockchain is used in the area of payment transactions, it can help reduce costs.
- This also enables the reporting of transactions to be optimized.
Disadvantages
In addition to these advantages, however, the use of blockchain technology also has some disadvantages:
- So far, the technology has not yet been broadly adopted, so there are currently only a few complete solutions. Implementation requires effort and expert knowledge, which is currently rare.
- The transaction speed of this technology is currently very low. Above all, the transaction backlog on the Bitcoin blockchain made it clear in the past that the currency is not suitable for traditional payment transactions.
- In addition, there are challenges in terms of storage space, because a blockchain is continuously growing with new transactions and requires more storage space.
In which areas can a blockchain be used?
Over the past year, the blockchain became known through cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin in particular was very popular and was able to record an enormous increase in value, which has now been put into perspective again. Accordingly, the technology is used in the field of means of payment. But traditional banks also rely on the technology and integrate it into payment systems. This enables costs to be reduced and transactions to be documented in a comprehensible manner. With BigchainDB there is already a scalable blockchain database that can compensate for some of the disadvantages described. The blockchain can manage a million write operations per second and store several petabytes of data. The blockchain can generally be seen as the answer to changing customer needs in many areas. More and more users want to manage their personal data on their own. For this