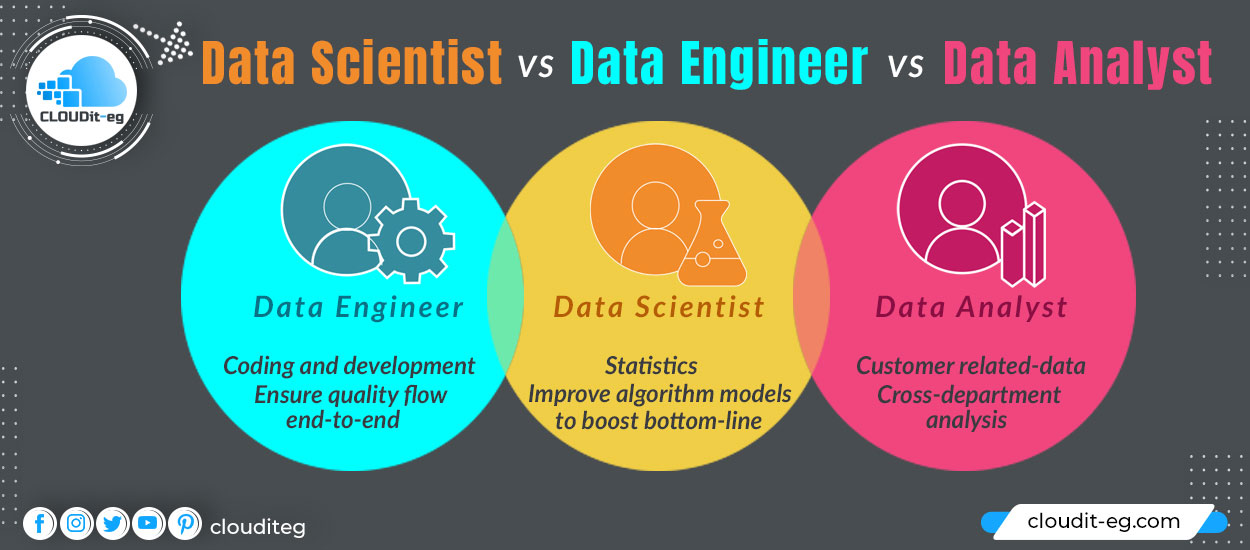
Data scientist vs data engineer vs data analyst. The first is for predicting future insights, The second is for developing & maintaining, The third is for taking profitable actions.
The profession of Data Scientist is making buzz lately. Harvard Business School magazine goes so far as to call it the sexiest profession of the 21st century.
Data Science remains a broad field with blurred outlines. This leads to the proliferation of new terms to designate new professions (or not that new!). Among these buzzwords, we find Data Scientist, Data Engineer, Data Analyst. These trades are sometimes unrecognized, which opens the door to confusion.
To remedy this, let’s take a closer look at what each profession aspires to and what are the differences that characterize them.
Data Analyst
A data analyst is someone who is able to interrogate data sources to make reports and graphical visualizations (pie charts, histograms, etc.). A Data Analyst has a strong understanding of the business domain in which he operates. This allows him to communicate better with people in the trade.
To better explore data, a Data Analyst is generally comfortable with statistical tools. However, he is not necessarily as “technically savvy” as a software engineer to process large volumes of data (Big Data).
Skills and tools: Excel, Access, SQL, SPSS, Table, Statistics …

Data Engineer
A Data Engineer is someone with a technical background in software development. He can be a Software Engineer who has converted to Big Data.
Data Engineers will set up Big Data systems to process them. They will opt for efficient storage tools such as NoSQL databases and will rely on Hadoop, Spark, Map / Reduce to properly process these large volumes of data.
Data Engineers will collect and transform data from different sources. This preparatory work will make it possible to have “clean” data, ready to be applied to them by machine learning techniques.
In other words, a Data Engineer’s job is to set the stage for a Data Scientist to use clean data to draw insights from it.
Skills and tools: SQL, NoSQL, Hadoop, Data Lake, Big Data, Spark, Software Engineering, Map / Reduce …

Data Scientist
A Data Scientist is a multidisciplinary profile whose primary mission will be to extract useful information (insights) from raw data. The job of the Data Scientist is at the intersection between Data Analyst and Data Engineer. While having business knowledge in the field in which he operates.
Indeed, a Data Scientist will explore and exploit the company’s data pools to apply machine learning techniques to them. It is therefore a form of Data Analysis that is extensive on large volumes of data. Exposure to the Big Data context requires a Data Scientist to be familiar with concepts like Map / Reduce, Hadoop, Data lake, etc …
The useful information sought by a Data Scientist is specific to a company and more generally to a business area. For this, a Data Scientist must be comfortable with the business area in which he operates. To do this, he will work alongside people in the trade to explore with them the various avenues for reflection.
Finally, a data scientist must be a good communicator to better communicate his reunion. For this, he will use different presentation media such as PowerPoint presentations, as well as graphic visualizations (histograms, pie charts, etc.) that speak to decision-makers.
Skills and tools: SQL, NoSQL, Python, R, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Statistics, Software Engineering …