Computing is the main function of an IT environment. The term is to be taken as a whole. Everything is calculated, from complex modeling to the display of a website, including the use of office tools. This function is performed by the data center or by individual machines in the case of office automation tools.
The common point to all these uses is the presence of all these elements on a company network. A remote network or local network is a connected whole.
However, there are scenarios where this connection to the network is severely degraded or even absent for an undefined period of time. We, therefore, speak of an intermittent network. This is not the result of a failure, but rather of a particular environment.
For example,
A mine or an oil platform. It is possible in these environments to perform some operations independently. Data entry or a report that does not strictly speak requires computing power.
In most cases, it is necessary to be able to rely on computing, processing, and storage machines capable of providing the service. These machines first process data, then secondly, and deferred consolidation (copy/transfer) of data as soon as the network is usable.
This edge computing is called edge computing. Decentralization of computing machines.
Be careful,
This is a very broad subject that can also meet the need for treatment “as close as possible” needs. Not just intermittent network environments. Last precision, Edge devices are obviously not there to replace the company’s Datacenter.
The heart of the calculation remains the Datacenter, the Edge comes in addition, even if certain Edge peripherals embed processors and memory in quantity. Interesting, but… how does it work and what scenario?
Situation
In this example, imagine an oil platform with low network capacity, prone to an outage, equipped with IoT sensors. These sensors are responsible for temperature and humidity measurements. In this simple scenario, the data is only used for statistical purposes. When the network is available, the bandwidth is very low. It is not possible to send all the data collected from all the sensors to the Datacenter.
All of these constraints therefore require:
– An edge computing system as close as possible to needs
– Data filtering to reduce the volume and only send data that is of real interest. Here, humidity levels above 80% and temperatures below 5 ° and above 50 °.
A parenthesis on the subject of data filtering with the Phi-Sat-1 project. Or how to keep only what is of value …
How to respond to these constraints?
By physically bringing to the site (the oil platform) a device that will cover these needs. An Azure Edge validated machine on which the necessary compute modules have been deployed.

To experience the concept, you don’t need to own a top-tier Edge device. A Raspberry PI 3 development board is sufficient to deploy a module and drive a few dozen sensors. The “Stream Analytics” module that I chose will be used for data filtering. Only temperature and humidity data within a certain threshold are kept, the rest is dropped. This filtering operation is not done on the company’s Datacenter (here, Azure in connection with the IoT Hub) but on the Raspberry (local) using the module.
The PI is prepared and registered as an Edge device in an IoT Hub (a centralization console for Azure IoT services).
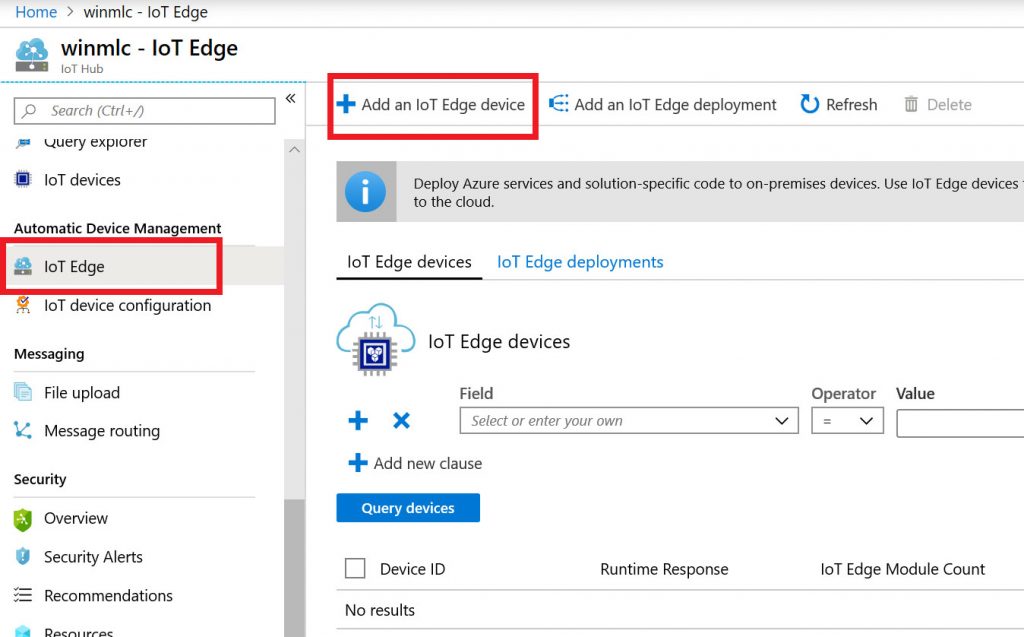
Then the module is deployed in the form of a container.
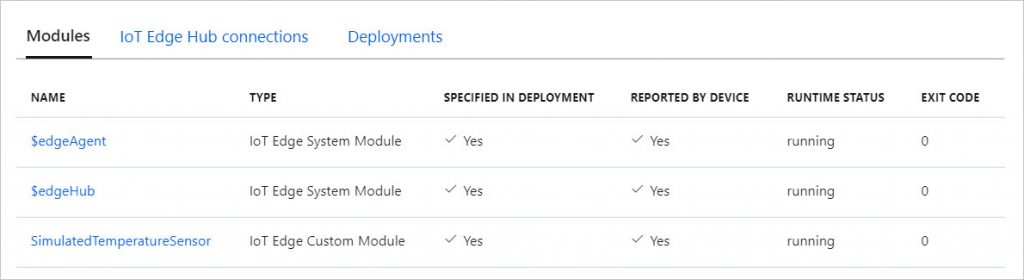
The IoT sensors are declared on the Edge machine which will perform data processing, storage when the network is unstable, and copying of filtered data when possible. That is when the network is available. Ultimately, the data is injected into the Azure Cloud.
In more advanced scenarios, the sensors are finely controlled by the Edge device, which can launch actions if necessary.
Available in other forms than IoT ( Azure Stack Edge is an example ), edge computing will become more and more present and will allow covering very specific use cases for which there was no, there is still very little time, no IT solution.
To sum up, a reminder of the important points
- Edge computing moves compute closer to needs.
- It covers several scenarios, including networks with very low connectivity.
- The Edge device can control the IoT sensors very finely (restart, update, etc.).