One of the hallmarks of big data is variety. This variety concerns several levels and one of the elements is the variety of data. In this article, we’ll take a look at the two types of data: Structured and unstructured data.
Structured Data
The term structured data generally means data having a defined type, format, and length. We can cite a few examples of structured data:
- Numbers
- Dates
- Strings
Several researchers specializing in Big Data claim that this type of (structured) data represents about 20% of existing data. However, structured data is the most manipulated data and is usually stored in relational databases.
Very often, SQL is used to query this data.
In companies, we collect structured data from different sources such as CRM and ERP.

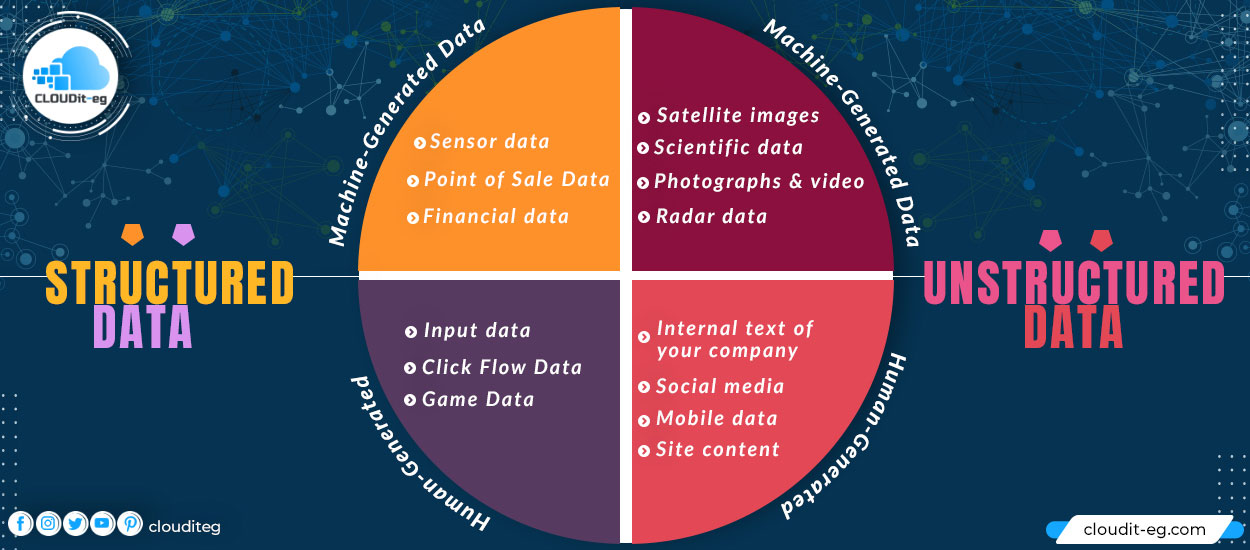
Sources of Structured Data
Structured data sources are divided into two categories:
1 – Machine-Generated Data:
This is the data generated automatically by the machine without any human intervention.
Machine-generated structured data includes the following:
- Sensor data: for example RFID tags, medical devices, and GPS data. Here we can take the example of tracking containers of products from one place to another. When the information is transmitted through the chip, it can go to a server and be analyzed. Companies are interested in this for supply chain management and inventory control.
- Point of Sale Data: When the cashier scans the barcode of any product, all data associated with that product is generated. If we look at the number of products sold per day, we realize the enormous amount of data generated.
- Financial data: Financial systems use predefined rules to automate processes and thus generate data. For example, stock data contains structured data such as company code (ISIN) and a dollar or euro value.
2- Human-Generated:
This is data generated by humans interacting with the computer during input, for example.
Human-generated structured data includes the following:
- Input data: This is data that a human could enter into a computer using a keyboard, for example.
- Click Flow Data: Every time you visit a site on the Internet when you click on a link, you generate data. This data can be analyzed to understand the behavior of site visitors.
- Game Data: Every move you make in a game can be recorded. This can be useful in understanding how end users move around a game portfolio.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is data that does not follow a specific typology or format. As said before, 80% of the available data is unstructured.
Unstructured data is therefore the vast majority of data that you will encounter. However, until recently, technology did not allow much of this data to be exploited other than to store or analyze it manually.

Sources of Unstructured Data
The good news is unstructured data is everywhere!
Like structured data, unstructured data is generated by the computer or by humans.
1 – Machine-Generated Data:
Here are some examples of machine-generated data:
- Satellite images: This includes meteorological data, data collected by states as part of satellite surveillance. Google Earth is a prime example.
- Scientific data: This includes seismic images, atmospheric data, and high-energy physics.
- Photographs and video: data generated by video surveillance systems for example.
- Radar data
2 – Human-Generated:
Here are some examples of human-generated data:
- Internal text of your company: for example, the text content in procedures, documentation, and email exchanges.
- Social media: All data generated on social networks such as comments on YouTube or “likes” on Instagram or even tweets.
- Mobile data: Text messages (SMS) or location data.
- Site content: For example, the content of this blog that I produce.